Geographic Information System (GIS) Technology
GIS is a collection of computer hardware, software, and geographic data for capturing, managing, analyzing, and displaying all forms of geographically referenced information. Geographical Information System (GIS) is a new and valuable tool of the 'information revolution' with the capability of combining attribute and spatial data with mapping systems and cartographic modeling tools.
It permits the acquisition, storage, analysis, management and presentation of large amounts of geographic or spatial data with the ai, of solving a geographic problem.
In the recent years, the application of GIS in business has grown rapidly. Major retailers, automobile dealerships, video rental companies, media organizations, and fast food corporations are just some of the many businesses around the world that have discovered the value of GIS. Research has shown that since more than 80 per cent of all information in an organization can be geographically referenced, business strategists are finding GIS to be an ideal tool for identifying and expanding markets, and increasing profits.
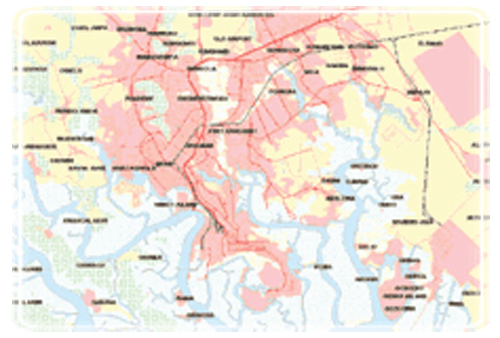
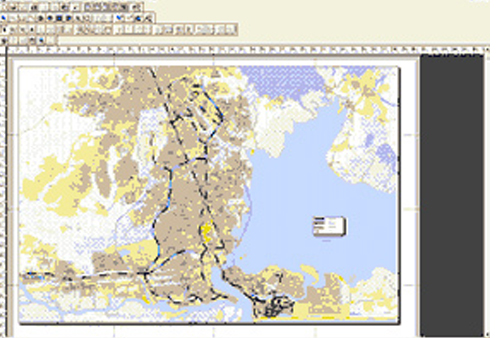
A GIS is most often associated with a maps. A map, however, is only one way you can work with geographic data in a GIS, and only one type of product generated by a GIS. This is important, because it means that a GIS can provide a great deal more problem-solving capabilities than using a simple mapping program or adding data to an online mapping tool (creating a "mash-up").
A GIS can be viewed in three ways:
1. The Database View: A GIS is a unique kind of database of the world—a geographic database (geodatabase). It is an "Information System for Geography." Fundamentally, a GIS is based on a structured database that describes the world in geographic terms.
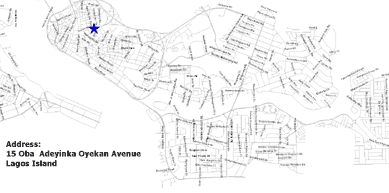
2. The Map View: A GIS is a set of intelligent maps and other views that show features and feature relationships on the earth's surface. Maps of the underlying geographic information can be constructed and used as "windows into the database" to support queries, analysis, and editing of the information. This is called geovisualization.

3. The Model View: A GIS is a set of information transformation tools that derive new geographic datasets from existing datasets. These geo-processing functions take information from existing datasets, apply analytic functions, and write results into new derived datasets.
Contact us today and let us show you how we can help you to draw on the power of visual analysis of GIS